Revolutionary Treatment for Post-Cosmetic Surgery Infections: How ALA-PDT Is Changing the Game for Dermatologists
2025-05-07 18:06Why Dermatologists Are Rethinking the Way They Treat NTM Infections
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infections after cosmetic procedures are increasing in dermatology clinics. These infections are resistant to antibiotics, difficult to treat, and prone to recurrence.
Treatment may last several months
High risk of antibiotic resistance and side effects
Recurrence rates up to 13%
Enter ALA-PDT — A Targeted, Drug-Enhancing, Tissue-Sparing Innovation
What is ALA-PDT?
ALA-PDT (5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy) activates a photosensitizer with light to kill pathogens, stimulate immunity, and promote healing.
Why ALA-PDT Works for NTM Infections
Oxidative destruction of pathogens
Improves antibiotic sensitivity
Stimulates immune clearance
Safe for aesthetic facial areas
Clinical Results: 100% Cure Rate in 10 Patients with No Recurrence
A case series of 10 women treated with surgical debridement + ALA-PDT + antibiotics showed:
100% cure rate
Reduced treatment time (as short as 8 days)
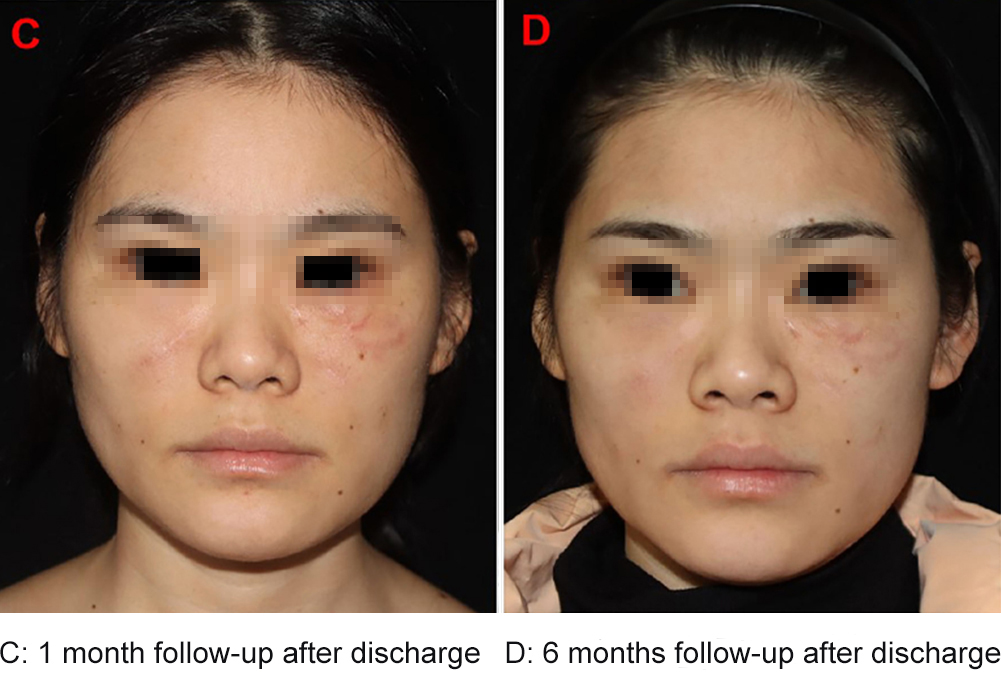
No recurrence after 6 months
Minimal side effects (mild, self-limiting)
Most Common Pathogens Treated
Mycobacterium abscessus
Mycobacterium chelonae
Mycobacterium fortuitum
Mycobacterium avium
Real Case Highlight: Salvaging the Face, Avoiding Scars
A 31-year-old woman with facial abscesses post-filler injections successfully recovered through debridement and ALA-PDT, avoiding scars and recurrence.
Medical History
On November 29, 2023, the patient underwent a cosmetic procedure involving collagen filler injection for tear trough correction at a local medical facility. Post-procedure, she developed persistent facial swelling and pain. Twenty-four days later, the filler was surgically removed; however, the swelling did not subside and was diagnosed as an abscess. Four days after filler removal, bilateral lower eyelid edema worsened. On December 19, 2023, incision and drainage of the abscess were performed. Bacterial culture confirmed infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Since then, the facial wound remained non-healing.
Clinical Presentation
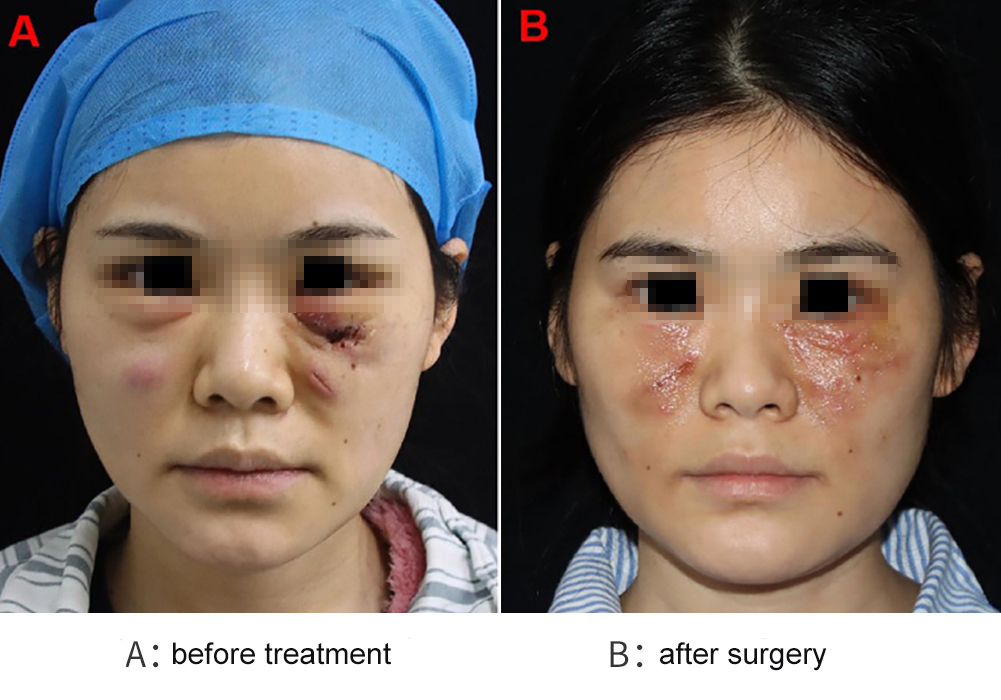
At admission, the patient presented with bilateral lower eyelid swelling with palpable fluctuance. Each lower eyelid contained a firm mass approximately 2 cm in diameter. The incision site showed indistinct margins and a small amount of purulent discharge (Figure A).
Treatment Course
➢ Debridement and Initial PDT Treatment
On January 25, 2024, the patient underwent surgical debridement. Starting the next day, she received weekly PDT sessions—three in total. The first two sessions caused pain exceeding 5 on the visual analog scale (VAS), requiring analgesic management. For subsequent sessions, preemptive analgesia was provided to alleviate pain. During this period, wound exudate cultures continued to test positive for Mycobacterium abscessus, and antibiotic therapy was adjusted based on susceptibility testing.
➢ Further Debridement and Treatment Interruption
Repeat surgical debridement was performed on February 18 and March 14, 2024. At the April 5 follow-up, the patient declined further surgery and PDT, opting instead for a one-week course of antibiotics, which was later discontinued due to adverse reactions.
➢ Final Debridement and Resumption of PDT
On May 8, 2024, the patient underwent a second abscess incision and drainage procedure with analgesia support, followed by another session of PDT. On June 17, she underwent scar excision, necrotic tissue removal, and a final PDT session.
Why You Should Consider PDT in Your Practice
Clinical Advantages for Dermatologists
Shorter antibiotic courses
Improved adherence
Low side effect risk
High patient satisfaction
Outpatient-friendly protocol
Key Takeaways for Dermatology Professionals
| Feature | Traditional Approach | PDT-Enhanced Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 3–14 months | 8–98 days |
| Recurrence | Up to 13% | 0% |
| Pain Management | Limited | Controlled |
| Tissue Preservation | Poor | Excellent |
| Drug Resistance | High | Reduced |
Final Thoughts
As NTM infections continue to rise in cosmetic dermatology, innovative multimodal treatments are urgently needed. ALA-PDT offers a scientifically sound, clinically proven solution that dermatologists can confidently integrate into their practice. Its ability to shorten recovery, preserve appearance, and eliminate infection is a game-changer in skin infection management.


