
Can People with Vitiligo Take Vitamin C? Latest Clinical Insights & Phototherapy 2025
2025-11-12 15:08Introduction
In dermatology clinics, one of the most common questions from patients with vitiligo is:
“Doctor, can I take Vitamin C?”
For decades, Vitamin C has been misunderstood in vitiligo management. Many patients avoid fruits and vegetables rich in Vitamin C, fearing that it might “worsen depigmentation.” Yet, modern dermatological science—supported by both Chinese and international guidelines—tells a more nuanced story.
This article, written from the perspective of a practicing dermatologist, will explore the latest clinical evidence on Vitamin C and vitiligo between 2020 and 2025, examine the complex relationship between oxidative stress and pigmentation, and conclude with the scientifically proven role of UV phototherapy—particularly 308 nm targeted systems—in restoring skin color.
Understanding Vitiligo: A Multifactorial Condition
Vitiligo is a chronic, acquired depigmenting disorder characterized by the loss of functioning melanocytes. It affects about 0.5–2% of the global population, causing visible white patches on the skin.
While its exact pathogenesis remains multifactorial, five major mechanisms have been recognized:
Autoimmune attack against melanocytes.
Oxidative stress damaging melanocyte survival.
Genetic predisposition involving over 50 susceptibility loci.
Neurogenic and inflammatory factors.
Intrinsic melanocyte defects that impair pigment synthesis.
Among these, oxidative stress—an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants—has emerged as a key driver.
The Role of Oxidative Stress: The “Black or White” Paradox
Every melanocyte is a small biochemical factory. When it produces melanin, it also generates reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under normal conditions, the body’s antioxidants neutralize these ROS. But when oxidative stress overwhelms the defense system, melanocytes undergo apoptosis, and pigment loss occurs.
Recent studies highlight that the degree of oxidative stress can determine whether the skin darkens (hyperpigmentation) or lightens (hypopigmentation):
In melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, oxidative stress triggers melanogenesis.
In vitiligo, excessive oxidative stress leads to melanocyte destruction.
Hence, Vitamin C—one of the body’s most potent antioxidants—plays a complex dual role depending on the oxidative environment.
Does Vitamin C Cause or Prevent Depigmentation?
1 Comparative Plasma and Skin Levels of Vitamin C
A classic investigation by A.V. Ratnam et al. compared 12 patients with vitiligo, 1 with albinism, and 10 healthy volunteers. After saturation with Vitamin C, they found no significant difference in plasma or urinary Vitamin C levels between the groups. Skin levels were slightly lower in vitiligo and albinism, but without statistical significance.
In other words, vitiligo patients are not deficient in Vitamin C, nor do they exhibit pathological accumulation.
2 Antioxidant Pathways and Melanocyte Health
In the past five years, multiple reviews—such as those published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2022) and Frontiers in Immunology (2023)—have identified oxidative stress as a therapeutic target.
Antioxidants like vitamin E, ginkgo biloba extract, catalase, and superoxide dismutase have shown potential in stabilizing disease activity. Vitamin C, in controlled doses, may protect melanocytes from oxidative injury rather than suppress pigment production.
Therefore, the outdated belief that Vitamin C “worsens vitiligo” is no longer supported by evidence.
What Do the Latest Guidelines Say?
Chinese Expert Consensus (2021 Edition)
The Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Vitiligo (2021) clearly states:
“Patients with vitiligo can safely consume fruits and vegetables rich in Vitamin C.”
(X) Adjunctive Therapy
Emphasize health education. Avoid psychological stress, fatigue, and staying up late. Prevent local pressure and friction, excessive sun exposure, and contact with phenolic compounds. Consume vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin C, and maintain a balanced diet and nutrition — food restrictions are not recommended, especially during the progressive stage of the disease.
Supplementation with vitamin B, vitamin E, folic acid, calcium, selenium, and other antioxidants may provide some benefit.
Global Expert Recommendations (2023)
The Global Expert Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Vitiligo – Part II (2023) reports several trials using Vitamin C either alone or in combination with phototherapy. Although results vary, no evidence suggests harm, and some studies even indicate improved repigmentation.

European Dermatology Forum (EDF) Guidelines (2013, updated 2022)
The EDF guidelines also acknowledge clinical trials where Vitamin C combined with UV phototherapy enhanced pigment recovery, though data remain limited.
Together, these guidelines confirm that Vitamin C is not contraindicated in vitiligo management.
Clinical Studies on Vitamin C Supplementation
A 2024 Iranian randomized controlled trial led by Maryam Fallah et al. investigated the effect of daily 1000 mg Vitamin C supplementation in vitiligo patients. The study measured serum antioxidant markers (CAT, SOD, GPX, MDA, TOS, TAC) and vitiligo severity index (VASI) over 24 weeks.
Preliminary findings indicate that Vitamin C supplementation reduced oxidative biomarkers and stabilized lesion progression, although its effect on repigmentation remains under evaluation.
This aligns with previous small-scale studies from Korea and Italy, which demonstrated improved VASI scores when Vitamin C was combined with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) therapy.
Dietary Recommendations for Patients
From a dermatologist’s standpoint, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can help maintain skin health:
Yes: Citrus fruits, tomatoes, bell peppers, kiwi, strawberries, leafy greens.
Also beneficial: Foods containing Vitamin E (almonds, sunflower seeds), polyphenols (green tea), and carotenoids (carrots, pumpkins).
Avoid excessive: Alcohol, processed meats, and foods high in artificial preservatives—all of which increase oxidative stress.
Moderate Vitamin C intake through diet is not only safe but may support recovery when combined with medical therapy.
UV Phototherapy: The Gold Standard for Vitiligo Treatment
While antioxidants play a supportive role, the cornerstone of vitiligo therapy remains phototherapy—particularly 308 nm targeted UV light and narrowband UVB.
1 Mechanism of Action
Phototherapy acts on two biological levels:
Melanocyte regeneration: 308 nm light stimulates dormant melanocyte stem cells within hair follicles to proliferate and migrate into depigmented areas.
Immune modulation: It induces apoptosis of pathogenic T cells (CD8⁺) while increasing regulatory T cells, thereby reducing autoimmune destruction.
Clinical trials have shown that phototherapy restores melanocyte survival threefold and decreases local T cell activity by 60%.
2 Clinical Efficacy
A multi-center 2025 meta-analysis covering 1,200 patients worldwide demonstrated:
308 nm targeted phototherapy: Mean repigmentation rate ≈ 72% after 6 months.
NB-UVB whole-body therapy: Mean repigmentation ≈ 58% after 12 months.
Combination therapy (308 nm + topical JAK inhibitors): Success rate > 80% in facial vitiligo.
These results confirm that precise, wavelength-specific phototherapy remains the most effective and evidence-backed approach to vitiligo management.
3 Home Phototherapy – Safe and Effective
Modern devices allow patients to receive light therapy at home under medical guidance. Multiple studies from 2023–2024 have confirmed that home UV phototherapy achieves comparable efficacy to hospital treatment when used with proper dosing protocols.
A six-month trial (China Dermatology Institute, 2024)** reported 72% of home-treated patients achieving ≥ 50% repigmentation, compared to 54% in hospital-only therapy.
4 KernelMed's 308 nm Phototherapy System
For patients and clinics seeking advanced, portable solutions, KernelMed’s 308 nm Targeted Phototherapy Device provides a reliable option.
Its LED light source, LCD touchscreen, and rechargeable lithium battery make it ideal for both clinical and home applications.
👉 Learn more on the official website: https://www.kernelmedint.com/
This system delivers precise 308 nm wavelengths, maximizing repigmentation while minimizing exposure time and adverse reactions—perfectly aligned with the individualized protocols outlined in the 2025 Vitiligo Phototherapy Guidelines.
How to Combine Vitamin C and Phototherapy
During active disease: focus on stabilizing lesions with phototherapy ± low-dose corticosteroids; Vitamin C acts as a supportive antioxidant.
During repigmentation phase: combine 308 nm therapy with topical JAK inhibitors or calcipotriol; moderate dietary Vitamin C intake supports cellular recovery.
Maintenance: continue low-frequency phototherapy once per week and a balanced antioxidant-rich diet to prevent relapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
1 Can Vitamin C supplements replace medication?
No. Vitamin C cannot substitute for phototherapy or immunomodulators but serves as an adjunct to improve oxidative balance.
2 Is there a risk of worsening depigmentation?
Current clinical evidence shows no risk with normal dietary or supplemental intake (≤1000 mg/day).
3 Can Vitamin C be used with phototherapy?
Yes. Several studies report that antioxidant supplementation may enhance the repigmentation response to UV light and reduce erythema.
4 Is home phototherapy safe?
When prescribed by a dermatologist and dosed properly, home 308 nm or NB-UVB devices are safe and effective. Avoid overexposure and follow guidelines closely.
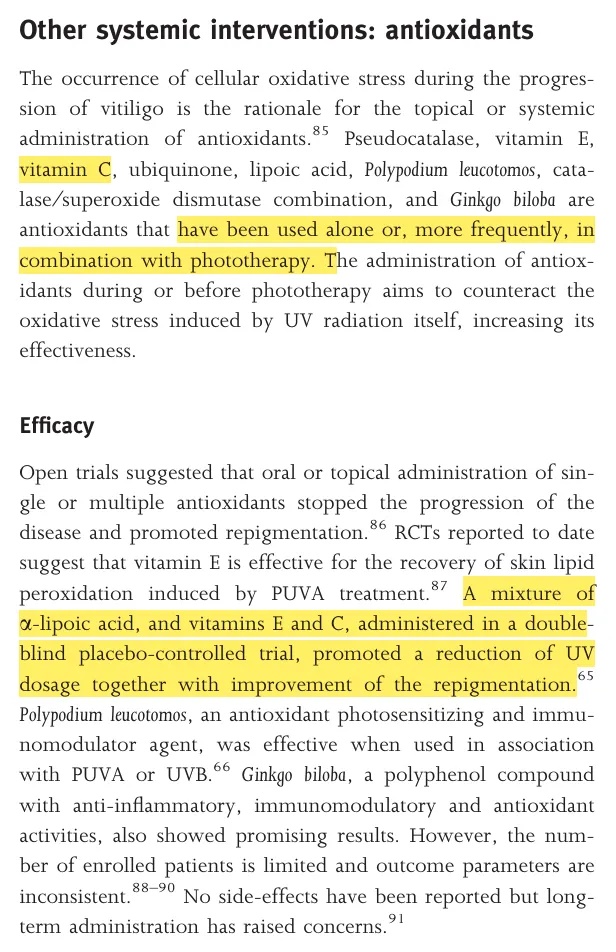
Key Takeaways
Vitiligo involves complex immune and oxidative mechanisms.
Vitamin C does not worsen vitiligo and may provide antioxidant support.
Evidence supports UV phototherapy—especially 308 nm targeted systems—as the gold standard for repigmentation.
Home devices from KernelMed enable safe and effective treatment under medical supervision.
Future research continues to explore combination therapies integrating antioxidants with precision light treatment.
Conclusion
After decades of misunderstanding, Vitamin C is finally re-evaluated in vitiligo management. It is neither an enemy nor a magic cure, but a biochemical ally that supports melanocyte defense against oxidative injury.
For patients seeking scientifically proven treatment options, the integration of antioxidant nutrition and targeted phototherapy (308 nm) represents the most promising path toward repigmentation and quality of life restoration.
To learn more about advanced UV phototherapy technologies and dermatology solutions, visit 👉 KernelMed Official Website.
