
Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in Clinical Dermatology: Precision, Applications, and Real-Time Diagnosis
2026-02-12 17:02The Diagnostic Gray Zone in Modern Dermatology
Every dermatologist is familiar with the uncomfortable middle ground.
A pigmented lesion that is not clearly malignant—yet not convincingly benign.
A hypopigmented patch that does not fully fit vitiligo—yet cannot be dismissed.
A chronic plaque that resembles psoriasis—but lacks classic features.
In these situations, the question is not whether histopathology works. It does.
The real question is whether biopsy is always the first—and best—step.
Over the past decade, Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) has reshaped how we approach this diagnostic gray zone. As a form of in vivo confocal microscopy, it enables real-time skin imaging at near-histologic resolution, providing non-invasive skin diagnosis without disrupting tissue integrity.
RCM does not replace biopsy.
It refines the decision of when, where, and whether biopsy is necessary.
With the advancement of high-resolution dermatology imaging systems designed for precision skin imaging and structured clinical workflows, RCM has evolved from a research tool into a practical component of daily dermatologic practice.
Core Advantages of Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in Clinical Practice
Reflectance Confocal Microscopy offers several clinically meaningful advantages that directly influence diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency.
Non-Invasive Skin Diagnosis
RCM allows in vivo visualization of epidermal and superficial dermal structures without tissue removal. This is particularly important in cosmetically sensitive areas and in patients requiring repeated assessment.
Real-Time Skin Imaging at Cellular Resolution
Unlike traditional histopathology, RCM provides immediate imaging results during consultation. This shortens diagnostic cycles and enhances patient communication.
Repeatability and Dynamic Monitoring
Because the skin remains intact, lesions can be evaluated repeatedly at the same site. This makes RCM especially valuable for longitudinal monitoring of inflammatory and pigmentary disorders.
High-Resolution Dermatology Imaging with Wide Scanning Capability
Modern RCM platforms provide broad scanning areas and strong image contrast, facilitating identification of characteristic architectural and cellular changes across heterogeneous lesions.
Well-integrated systems optimized for precision skin imaging and real-time diagnosis allow structured incorporation into outpatient dermatology workflows without increasing procedural burden.
Clinical Applications of RCM in Dermatology
1. A Tool for Clinical Screening
RCM is particularly valuable in the evaluation of melanocytic lesions, including:
Intradermal nevus
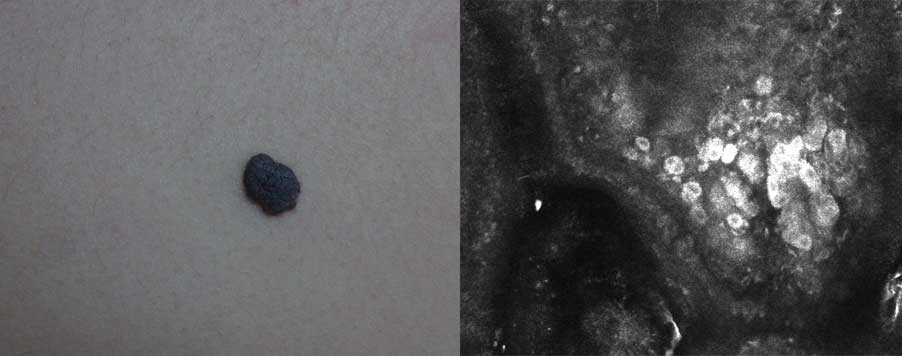
Junctional nevus
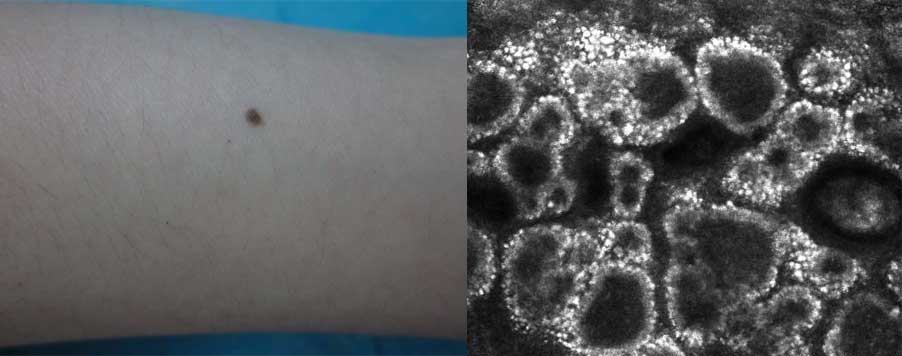
Through detailed visualization of melanocyte distribution and dermal nesting patterns, RCM skin imaging helps distinguish benign from suspicious features, reducing unnecessary excisions while maintaining diagnostic safety.
In high-volume dermatology settings, this contributes to more structured and evidence-based lesion management.
2. Non-Invasive Histologic Subtyping of Skin Disorders
Melasma: Clinical Value of RCM-Based Classification
Melasma presents heterogeneous histologic patterns that directly influence treatment response.
Using in vivo confocal microscopy, melasma can be classified into:
Epidermal type
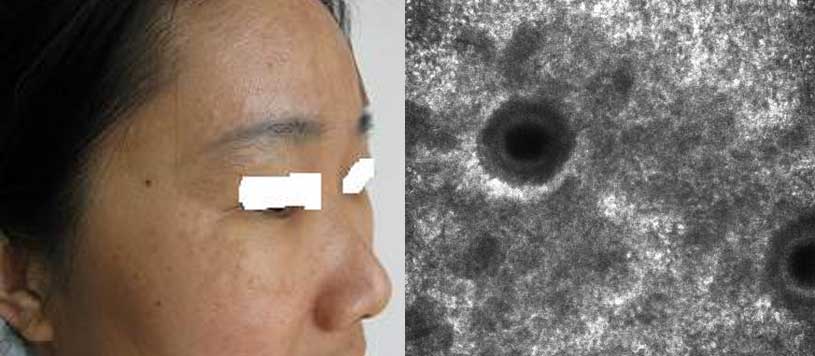
Mixed type – epidermal predominant
Mixed type – dermal predominant
RCM-based classification improves therapeutic planning:
Epidermal-predominant cases respond more predictably to topical depigmenting therapy.
Dermal-predominant involvement may require laser or energy-based modalities.
This form of non-invasive skin diagnosis supports personalized treatment strategies and avoids trial-and-error approaches.
3. Biopsy Site Localization
One of the most practical advantages of Reflectance Confocal Microscopy is RCM biopsy guidance.
In large or morphologically heterogeneous lesions, selecting the most representative biopsy site can be challenging. RCM allows clinicians to identify areas of cellular atypia or architectural disruption before tissue sampling.
This improves diagnostic yield and reduces the likelihood of repeat procedures.
For institutions integrating high-resolution dermatology imaging systems into their diagnostic pathway, this precision contributes to measurable improvements in workflow efficiency.
4. Diagnostic and Differential Diagnostic Support
RCM provides strong diagnostic clues in a wide spectrum of dermatologic conditions.
Seborrheic Keratosis vs. Verruca Plana
Differences in epidermal architecture and keratinocyte morphology assist differentiation.
Folliculitis vs. Molluscum Contagiosum
Visualization of follicular inflammation versus characteristic molluscum structures supports accurate diagnosis.
Erythema Annulare vs. Psoriasis
RCM reveals variations in epidermal thickness and inflammatory distribution.
Pityriasis Rosea vs. Psoriasis
Subtle structural differences can be appreciated without immediate biopsy.
Differential Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Disorders
Hypopigmented lesions frequently require careful evaluation. RCM assists in differentiating:
Vitiligo
Nevus depigmentosus
Nevus anemicus
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Key confocal evaluation parameters include:
Presence of fungal hyphae in the stratum corneum
Epidermal atrophy
Degree of melanocyte loss
Clarity of lesion borders
For vitiligo, real-time visualization of melanocyte depletion provides objective confirmation and supports therapeutic monitoring.
5. Dynamic Follow-Up and Treatment Evaluation
The role of Reflectance Confocal Microscopy extends beyond diagnosis into longitudinal disease management.
Psoriasis
Reduction in inflammatory infiltrates and normalization of epidermal structure can be observed during therapy.
Vitiligo
Monitoring melanocyte regeneration provides objective treatment endpoints.
Actinic Keratosis
Assessment of atypical keratinocyte resolution assists in evaluating non-surgical treatments.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
RCM for basal cell carcinoma supports margin assessment and post-treatment surveillance, reducing unnecessary surgical intervention.
Through non-invasive, repeatable in vivo imaging, RCM strengthens evidence-based follow-up strategies.
Integrating RCM Into Modern Dermatology Practice
As precision medicine becomes central to dermatology, non-invasive diagnostic imaging is no longer optional in advanced centers.
High-resolution Reflectance Confocal Microscopy systems designed for precision skin imaging and real-time diagnosis allow structured integration into outpatient workflows. When evaluating a platform, clinicians and institutions should consider:
Image clarity and contrast resolution
Scanning field capability
Data management systems
Workflow compatibility
Well-engineered RCM technology enhances diagnostic confidence while maintaining procedural efficiency—an important consideration for both clinical specialists and institutional decision-makers.
